
One reference that explains the math behind a geometric standard deviation is found on Wikipedia: How you calculate a geometric standard deviation, however, depends on which resource you are referencing. How you calculate the geometric mean is rather easy-you use the GEOMEAN function built into Excel. The place that a geometric mean is most often used (and, therefore, a geometric standard deviation) is when calculating investment returns over time, especially when the returns involve compound interest.
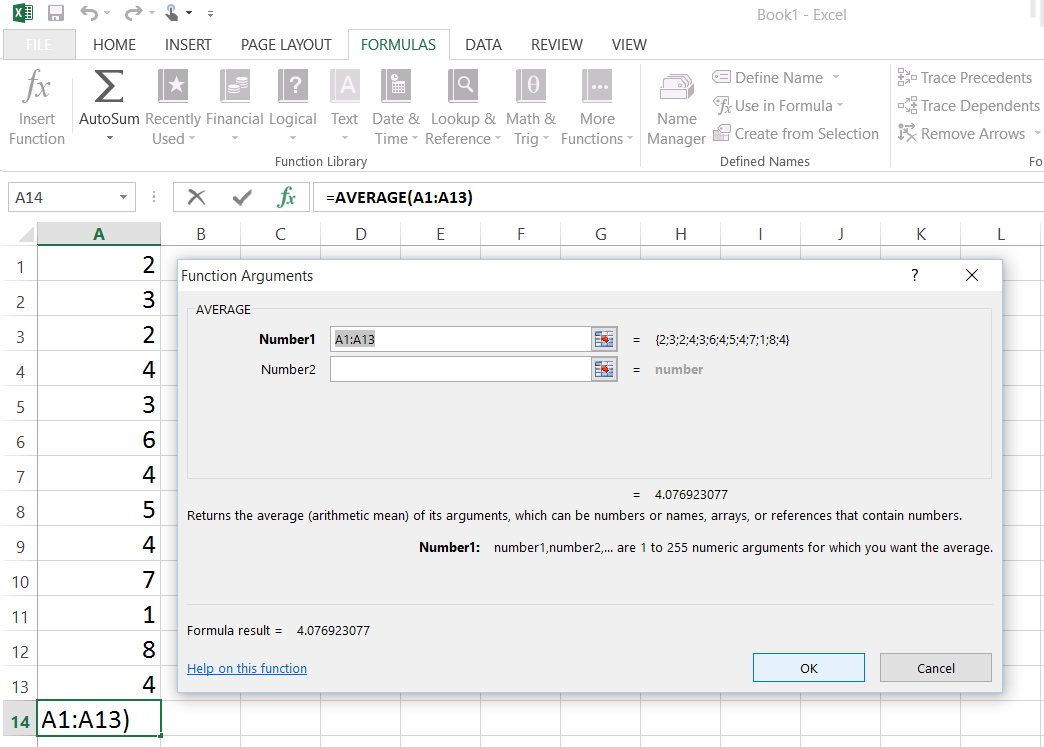
MEAN AND STANDARD DEVIATION EXCEL HOW TO
He cannot seem to figure out how to calculate the geometric standard deviation, however. He uses built-in Excel functions to calculate many of these, such as the geometric mean. The data set must be larger than 5 for a meaningful result.Jim has a set of data on which he needs to calculate some statistical information. The data set for %RDS must be based around one set of results, it is not applicable when there are different discrete sets of results. The main limitation is when the average is very small (<1) and a small variation in the set of data will result in a large result. Percent relative standard deviation is popular but there are limitations to the statistical method. The calculation from the previous example would be expressed as: Relative Standard Deviation Excel Limitations
=(STDEV(population)/(AVERAGE(population))*100 The short version for the left table is to combine the average and SD calculation into one function and this would read:
MEAN AND STANDARD DEVIATION EXCEL FULL
The image on the left displays the full calculation while the right image displays the numerical values.
This following %RSD example is based upon a data set of 5 values. The final stage of the calculation is to express the result as a percent which the *100 does.

The AVERAGE function calculates the mean of the data set while the STDEV calculates the standard deviation (SD) of the data. The excel %RSD calculation requires two functions Average and STDEV. The main use for %RSD is in analytical chemistry and is routinely used to assess the variation of sets of data. The %RSD function is popular with non-statisticians as the interpretation is based on a percent result and not some abstract value. %RSD (relative standard deviation) is a statistical measurement that describes the spread of data with respect to the mean and the result is expressed as a percentage. The result is expressed as an percentage, with a low number (<2.5%) indicating a small spread of values and a high value indicating a significant spread of results. In the cell where the formula is written a value between 0-100 will be reported. The above %RSD example has been entered into the Excel formula bar and will calculate the percent relative standard deviation of the 5 value data set E6 to E11. = (STDEV(Data Range) / AVERAGE(Data Range))*100 To calculate the %RSD in Microsoft Excel a short formula must be used: %RSD is a powerful tool to statistically inspect the variation in sets of data but a specific function is not available in Excel 2003, 2007 or even 2010. Percentage relative standard deviation is a widely used statistical tool but strangely there is no automated function in any version of Microsoft Excel. This guide will detail how to calculated the relative standard deviation (%RSD) using Excel, then walk through a worked example and finally detail the limitations of the calculation. Excel and Relative Standard Deviation %RSD


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
